Both the orientation of the cotyledons on the medium and the pH of the induction medium have a very strong effect on somatic embryogenesis. In the examples below, the cotyledons on the top row were placed on the medium with their flat side up, while those on the bottom row were placed on the medium with their flat side down. The cotyledons on the left are on pH 5.8, while those on the right are on pH 7.0:
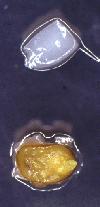

For more information on pH, see:
P. A. Lazzeri, D. F. Hildebrand, and G. B. Collins. 1987. Soybean somatic embryogenesis: effects of nutritional, physical and chemical factors. Plant Mol.Biol.Rep. 10:209-220.
Komatsuda,T. and S.-W.Ko. 1990. Screening of soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merrill] genotypes for somatic embryo production from immature embryo. Japan J. Breed. 40:249-251.
E. R. Santar�m, B. Pelissier, and J. J. Finer. 1997. Effect of explant orientation, pH, solidifying agent and wounding on initiation of soybean somatic embryos. In Vitro Cell Dev.Biol.- Plant 33:13-19.
For more information on orientation, see:
L. M. Hartweck, P. A. Lazzeri, D. Cui, G. B. Collins, and E. G. Williams. 1988. Auxin-orientation effects on somatic embryogenesis from immature soybean cotyledons. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol. 24:821-828.
J. P. Ranch. 1993. The potential for synthetic soybean seed. In: Synseeds: Applications of Synthetic Seeds to Crop Improvement, edited by K. Redenbaugh, Boca Raton, FL:CRC Press, p. 329-350.
E. R. Santar�m, B. Pelissier, and J. J. Finer. 1997. Effect of explant orientation, pH, solidifying agent and wounding on initiation of soybean somatic embryos. In Vitro Cell Dev.Biol.- Plant 33:13-19.
